Debt Mutual Funds
- Total Funds 414
- Average annual returns 3.22%
What is Debt Mutual Funds?
Debt Mutual funds belong to the conservative category in mutual funds that aims to generate returns by investing in fixed-income securities like corporate and government bonds and other money-market instruments. The debt mutual funds have a pre-determined maturity date and interest rate where the investor earns profits at the time of maturity.
- The average returns of debt funds range between 7%-10% outperforming traditional fixed deposits.
- Debt mutual funds offer low volatility with minimal risk.
- The best-recommended time for investment is 1-3 years for fixed-income stability.
Top Performing Debt Funds in India for High Returns
Returns
SIP Returns
Risk
Information
NAV Details
Data in this table : Get historical returns. If 1Y column is 10% that means, fund has given 10% returns in last 1 year.
Select date points :
Submit| Fund Name | AUM (Cr.) | Fund Age | 1W | 1M | 3M | 6M | YTD | 1Y | 2Y | 3Y | 5Y | 10Y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 511.89 | 16 years | 0.09% | 0.12% | 0.97% | 2.25% | 0.11% | 19.77% | 13.24% | 10.94% | 8.53% | 7.14% | Invest | |
| 205.76 | 22 years | -0.6% | -0.52% | 0.21% | 1.29% | -0.55% | 19.7% | 13.51% | 14.26% | 10.95% | 7.72% | Invest | |
| 1091.72 | 10 years | 0.12% | 3.37% | 4.65% | 6.82% | 3.39% | 16.6% | 14.19% | 11.78% | 9.78% | 8.48% | Invest | |
| 2904.91 | 16 years | 0.02% | 1.62% | 2.55% | 4.18% | 1.59% | 11.97% | 11.07% | 9.82% | 12.2% | 8.67% | Invest | |
| 106.96 | 10 years | 0.1% | 5.17% | 6.05% | 7.82% | 5.15% | 11.54% | 8.76% | 7.66% | 27.12% | 2.02% | Invest | |
| 5919.75 | 15 years | 0.17% | 0.28% | 1.61% | 3.87% | 0.33% | 9.1% | 8.46% | 8.43% | 7.33% | 7.84% | Invest | |
| 137.72 | 11 years | 0.04% | 0.02% | 0.84% | 2.04% | 0.01% | 8.93% | 8.46% | 8.17% | 8.9% | 3.36% | Invest | |
| 1338.11 | 28 years | 0.15% | 0.07% | 1.08% | 2.32% | 0.12% | 8.83% | 8.06% | 7.58% | 6.14% | 7.22% | Invest | |
| 155.57 | 11 years | - | 0.16% | 1.04% | 2.14% | 0.14% | 8.7% | 7.88% | 9.19% | 6.75% | 5.69% | Invest | |
| 43.51 | - | 0.71% | 1.25% | 2.14% | 4.18% | - | 8.64% | 7.51% | 6.36% | 5.83% | 6.73% | Invest | |
| 43.51 | - | 0.71% | 1.25% | 2.14% | 4.18% | - | 8.64% | 7.51% | 6.35% | 5.83% | 6.81% | Invest | |
| 32187.70 | - | 0.15% | 0.34% | 1.34% | 2.78% | 0.34% | 8.62% | 7.37% | 7.38% | 6.2% | 6.62% | Invest | |
| 32187.70 | - | 0.15% | 0.34% | 1.34% | 2.78% | 0.34% | 8.62% | 7.37% | 7.38% | 6.2% | 6.62% | Invest | |
| 706.86 | 15 years | 0.28% | 0.35% | 1.15% | 3.37% | 0.36% | 8.52% | 7.58% | 7.65% | 5.84% | 6.71% | Invest | |
| 1015.83 | 20 years | 0.19% | 0.22% | 1.17% | 2.85% | 0.24% | 8.45% | 8.31% | 8.22% | 8.4% | 6% | Invest | |
| 2014.86 | 11 years | 0.33% | 0.22% | 1.18% | 3.26% | 0.24% | 8.28% | 8.21% | 8.07% | 6.55% | 6.98% | Invest | |
| 5767.12 | 21 years | 0.14% | 0.07% | 1.25% | 3.11% | 0.09% | 8.22% | 8.08% | 7.83% | 6.81% | 7.45% | Invest | |
| 368.01 | 11 years | 0.11% | 0.09% | 1.23% | 3.24% | 0.09% | 8.21% | 8.05% | 7.75% | 6.74% | 6.79% | Invest | |
| 973.76 | 15 years | 0.14% | 0.21% | 1.11% | 2.5% | 0.21% | 8.17% | 7.76% | 7.57% | 6.11% | 6.66% | Invest | |
| 3368.00 | 6 years | 0.19% | 0.23% | 1.19% | 2.6% | 0.22% | 7.89% | 8% | 7.79% | 6.48% | - | Invest |
| Fund Name | AUM (Cr.) | Risk | 1W | 1M | 3M | 6M | YTD | 1Y | 2Y | 3Y | 5Y | 10Y |
|---|
| Fund Name | Feb-2026 | Jan-2026 | Dec-2025 | Nov-2025 | Oct-2025 | Sep-2025 | Aug-2025 | Jul-2025 | Jun-2025 | May-2025 | Apr-2025 | Mar-2025 |
|---|
| Fund Name | 2026-Q1 | 2025-Q4 | 2025-Q3 | 2025-Q2 | 2025-Q1 | 2024-Q4 | 2024-Q3 | 2024-Q2 | 2024-Q1 | 2023-Q4 | 2023-Q3 | 2023-Q2 |
|---|
| Fund Name | 2026 | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 |
|---|
| Fund Name | AUM (Cr.) | Risk | 1W | 1M | 3M | 6M | YTD | 1Y | 2Y | 3Y | 5Y | 10Y |
|---|
| Fund Name | AUM (Cr.) | Initial NAV | Final NAV | NAV Change | Absolute Ret. | Annalized Ret. |
|---|
| Fund Name | AUM (Cr.) | Risk | 6M | 1Y | 2Y | 3Y | 5Y | 10Y | From Launch | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 511.89 | Moderately High |
0.92%
|
9.39%
|
14.09%
|
12.77%
|
10.4%
|
7.76%
|
7.64%
|
Invest | |
| 205.76 | Moderately High |
0.83%
|
6.23%
|
13.89%
|
14.47%
|
13.12%
|
9.27%
|
7.97%
|
Invest | |
| 1091.72 | Moderately High |
1.29%
|
7.37%
|
11.6%
|
11.42%
|
10.21%
|
8.54%
|
8.46%
|
Invest | |
| 2904.91 | Moderately High |
1.11%
|
6.01%
|
9.46%
|
9.58%
|
10.98%
|
9.37%
|
9.01%
|
Invest | |
| 106.96 | High |
0.93%
|
4.99%
|
5.5%
|
5.74%
|
16.92%
|
8.06%
|
7.06%
|
Invest | |
| 5919.75 | High |
1.36%
|
7.33%
|
8.2%
|
8.31%
|
7.78%
|
7.69%
|
7.97%
|
Invest | |
| 137.72 | Moderately High |
0.94%
|
6.73%
|
8.22%
|
8.2%
|
7.81%
|
4.23%
|
4.09%
|
Invest | |
| 1338.11 | Moderate |
1%
|
5.79%
|
7.62%
|
7.68%
|
6.96%
|
6.85%
|
7.75%
|
Invest | |
| 155.57 | Moderately High |
0.93%
|
4.91%
|
7.32%
|
7.82%
|
7.69%
|
6%
|
5.96%
|
Invest | |
| 43.51 | Low to Moderate |
-
|
-
|
1.92%
|
3.31%
|
4.07%
|
4.86%
|
5.43%
|
Invest | |
| 43.51 | Low to Moderate |
-
|
-
|
1.93%
|
3.31%
|
4.07%
|
4.87%
|
5.13%
|
Invest | |
| 32187.70 | Moderate |
0.97%
|
7.09%
|
7.01%
|
7.12%
|
6.82%
|
6.43%
|
36.08%
|
Invest | |
| 32187.70 | Moderate |
0.97%
|
7.09%
|
7.01%
|
7.12%
|
6.82%
|
6.43%
|
36.08%
|
Invest | |
| 706.86 | Moderately High |
1.05%
|
6.49%
|
7.23%
|
7.46%
|
6.58%
|
6.28%
|
6.96%
|
Invest | |
| 1015.83 | Moderately High |
1.06%
|
6.25%
|
7.75%
|
7.96%
|
7.78%
|
6.28%
|
6.68%
|
Invest | |
| 2014.86 | Moderate |
1.17%
|
6.38%
|
7.66%
|
8%
|
7.25%
|
6.73%
|
6.89%
|
Invest | |
| 5767.12 | Moderately High |
1.28%
|
6.48%
|
7.76%
|
7.86%
|
7.34%
|
7.25%
|
7.63%
|
Invest | |
| 368.01 | Moderately High |
1.23%
|
6.59%
|
7.67%
|
7.76%
|
7.23%
|
6.71%
|
6.77%
|
Invest | |
| 973.76 | Average |
0.9%
|
5.57%
|
7.16%
|
7.38%
|
6.9%
|
6.31%
|
6.86%
|
Invest | |
| 3368.00 | Low to Moderate |
0.99%
|
5.67%
|
7.21%
|
7.51%
|
7.05%
|
-
|
6.87%
|
Invest |
| Fund Name | Risk | Standard Deviation | Alpha | Beta | Sharpe Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderately High |
1.24%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
5.83%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
1.82%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
9.4%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| High |
70.74%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| High |
1%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
8.15%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderate |
1%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
2.7%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Low to Moderate |
1.435%
|
-
|
0.479%
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Low to Moderate |
1.435%
|
-
|
0.479%
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderate |
0.54%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderate |
0.54%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
1.99%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
3.73%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderate |
1.55%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
1.21%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Moderately High |
0.96%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Average |
0.68%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
| Low to Moderate |
1.07%
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Invest |
| Fund Name | Min SIP | Min Lumpsum | Expense Ratio | Fund Manager | Launch Date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
₹1000
|
₹5000
|
1.68%
|
Shriram Ramanathan
|
08-Oct 2009
|
Invest | |
|
₹100
|
₹100
|
1.18%
|
Vivekanand Ramakrishnan
|
13-May 2003
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹100
|
1.54%
|
Sunaina da Cunha
|
17-Apr 2015
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹1000
|
1.56%
|
Sunaina da Cunha
|
25-Mar 2009
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹5000
|
1.38%
|
Alok Singh
|
27-Feb 2015
|
Invest | |
|
₹100
|
₹100
|
1.41%
|
Manish Banthia
|
03-Dec 2010
|
Invest | |
|
₹100
|
₹5000
|
1.1%
|
Kinjal Desai
|
26-Jun 2014
|
Invest | |
|
₹500
|
₹10000
|
0.81%
|
Rahul Goswami
|
23-Jun 1997
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹1000
|
1.45%
|
Krishna Venkat Cheemalapati
|
04-Sep 2014
|
Invest | |
|
₹500
|
₹1000
|
0.97%
|
Gurvinder Singh Wasan
|
18-Mar 2013
|
Invest | |
|
₹500
|
₹1000
|
0.97%
|
Gurvinder Singh Wasan
|
24-Nov 2014
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹100
|
0.36%
|
Deepak Agrawal
|
14-Jul 2003
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹100
|
0.36%
|
Deepak Agrawal
|
14-Jul 2003
|
Invest | |
|
₹100
|
₹100
|
1.71%
|
Deepak Agrawal
|
11-May 2010
|
Invest | |
|
₹100
|
₹500
|
1.47%
|
Sushil Budhia
|
08-Jun 2005
|
Invest | |
|
₹100
|
₹100
|
1.63%
|
Deepak Agrawal
|
21-Mar 2014
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹5000
|
1.35%
|
Manish Banthia
|
15-Sep 2004
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹5000
|
1.57%
|
Devang Shah
|
15-Jul 2014
|
Invest | |
|
₹1000
|
₹5000
|
1.09%
|
Shriram Ramanathan
|
04-Dec 2010
|
Invest | |
|
₹100
|
₹100
|
0.63%
|
Deepak Agrawal
|
14-May 2019
|
Invest |
| Fund Name | Current NAV | Previous NAV | 1D NAV Change | 52- Week High NAV | 52- Week Low NAV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
33.2809
(03-02-2026)
|
33.2504
(02-02-2026)
|
0.09%
|
33.2809
|
27.8062
|
Invest | |
|
50.5998
(03-02-2026)
|
50.5503
(02-02-2026)
|
0.1%
|
50.8852
|
42.2853
|
Invest | |
|
24.1563
(03-02-2026)
|
24.1251
(02-02-2026)
|
0.13%
|
24.1563
|
20.7137
|
Invest | |
|
42.0102
(03-02-2026)
|
41.9468
(02-02-2026)
|
0.15%
|
42.0168
|
37.4917
|
Invest | |
|
13.2229
(03-02-2026)
|
13.2153
(02-02-2026)
|
0.06%
|
13.2229
|
11.86
|
Invest | |
|
33.3227
(03-02-2026)
|
33.3178
(02-02-2026)
|
0.01%
|
33.3259
|
30.5645
|
Invest | |
|
16.2646
(03-02-2026)
|
16.2377
(02-02-2026)
|
0.17%
|
16.2646
|
14.9245
|
Invest | |
|
103.1117
(03-02-2026)
|
102.9876
(02-02-2026)
|
0.12%
|
103.112
|
94.8866
|
Invest | |
|
1988.5938
(03-02-2026)
|
1986.294
(02-02-2026)
|
0.12%
|
1988.59
|
1829.12
|
Invest | |
|
40.0725
(27-01-2025)
|
()
|
0.31%
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
|
40.4031
(27-01-2025)
|
()
|
0.31%
|
-
|
-
|
Invest | |
|
4656.7062
(03-02-2026)
|
4653.6893
(02-02-2026)
|
0.06%
|
4656.71
|
4417.79
|
Invest | |
|
4656.7062
(03-02-2026)
|
4653.6893
(02-02-2026)
|
0.06%
|
4656.71
|
4417.79
|
Invest | |
|
30.7159
(03-02-2026)
|
30.7225
(02-02-2026)
|
-0.02%
|
30.7225
|
28.3331
|
Invest | |
|
36.4573
(03-02-2026)
|
36.4096
(02-02-2026)
|
0.13%
|
36.4573
|
33.6298
|
Invest | |
|
23.687
(03-02-2026)
|
23.6849
(02-02-2026)
|
0.01%
|
23.687
|
21.8962
|
Invest | |
|
46.6636
(03-02-2026)
|
46.6418
(02-02-2026)
|
0.05%
|
46.6638
|
43.1602
|
Invest | |
|
22.3067
(03-02-2026)
|
22.2910
(02-02-2026)
|
0.07%
|
22.3067
|
20.6263
|
Invest | |
|
29.6469
(03-02-2026)
|
29.6222
(02-02-2026)
|
0.08%
|
29.6469
|
27.4188
|
Invest | |
|
1569.3182
(03-02-2026)
|
1567.5967
(02-02-2026)
|
0.11%
|
1569.32
|
1455.84
|
Invest |
Debt Funds Return Calculator
Historical Returns
Future Value
Invested Amt.
+Net Profit
=Total Wealth
- Invested Amount
- Estimated Returns
- Invested Amount ₹43,855
- Interest Earned ₹6,145
Explore Other Popular Calculators
Types of Debt Mutual Funds





 Aditya Birla Sun Life Financial Planning Fund - Aggressive Plan - Regular Plan - Growth Option
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
VS
Aditya Birla Sun Life Financial Planning Fund - Aggressive Plan - Regular Plan - Growth Option
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
VS
 HDFC Multi-Asset Active FOF - Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
HDFC Multi-Asset Active FOF - Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
 Bandhan Focused Fund - Regular Plan - Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
VS
Bandhan Focused Fund - Regular Plan - Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
VS
 Aditya Birla Sun Life Focused Equity Fund -Growth Option
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
Aditya Birla Sun Life Focused Equity Fund -Growth Option
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
 LIC MF Money Market Fund Regular - Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
VS
LIC MF Money Market Fund Regular - Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
VS
 ICICI Prudential Money Market Fund Option - Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
ICICI Prudential Money Market Fund Option - Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
 Nippon India Banking and Financial Services Fund - Growth Plan - Growth Option
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
VS
Nippon India Banking and Financial Services Fund - Growth Plan - Growth Option
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
VS
 Invesco India Financial Services Fund - Retail Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
Invesco India Financial Services Fund - Retail Growth
3Y Returns 15.23 % (p.a.)
What are the Types of Debt Mutual Funds?
Here are several types of debt mutual funds, each with different risk levels and investment goals:
- Liquid Fund: Invests in very short-term debt instruments, ideal for parking emergency funds with low risk.
- Money Market Fund: Focuses on short-term instruments like Treasury bills and certificates of deposit, offering safe returns.
- Dynamic Bond Fund: This category of debt mutual funds has no boundaries on portfolio selection, and the securities can be included in any maturity period.
- Corporate Bond Fund: It invests in bonds issued by companies that give higher returns but with more risk compared to government securities.
- Banking and PSU Fund: Invests in bonds from banks and Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), offering moderate risk and return.
- Gilt Fund: More than 80% of the total money is invested in government securities with a maturity period of 10 years, making it a low-risk option with stable returns.
- Credit Risk Fund: In this category, a minimum of 65% of the money is invested in corporate bonds having ratings below the highest-rated instruments.
- Floater Fund: These funds keep their investment in floating rate debt securities that adjust with market interest rates, giving protection against interest rate fluctuations.
- Overnight Fund: It invests in the securities within the Mutual Funds having a maturity period of 1 day, offering minimal returns with very low risk.
- Ultra-Short Duration Fund: It invests in debt securities with a maturity duration of three to six months. It gives the chance for high returns in comparison to liquid funds.
- Low Duration Fund: It invests in money market instruments with a maturity period of 6 to 12 months. These funds are best suited for low-risk investors seeking moderate returns.
- Short Duration Fund: These funds give you a portfolio of debt instruments that have an average maturity period of 1-3 years.
- Medium Duration Fund: It invests in debt securities with maturities of 3 to 5 years, balancing risk and return.
- Medium to Long Duration Fund: These funds invest in bonds with maturities of 5 to 7 years. It gives the potential to make higher returns with increased risk.
- Long Duration Fund: This category has a portfolio with a maturity duration of more than 7 years, carrying higher interest rate risk but offering higher returns.
Each type has its own risk and return profile, making it important to choose one based on your investment goals, and risk tolerance.
Benefits of Investing in Best Debt Funds
Apart from gaining capital appreciation at low risk, there are several other benefits of investing in best debt mutual funds:
- Volatility in the Equity Market Cannot Affect the Investments: Debt funds invest in securities with fixed income like treasury bills, Government sectors, bonds, debentures and money market instruments. These instruments do not affect the equity market condition. The investments can prosper even if the equity market is falling.
- Portfolio Gets Stable: The volatility in the portfolio of the investor can be reduced to a great extent if a debt scheme is added to the portfolio. It adds stable gains even if the equity schemes drag the returns downwards in a portfolio. Hence, a balanced portfolio with equity and debt funds is less likely to face volatility.
- Easy Withdrawal: All the debt funds are open-ended and most of them charge no exit load. Investors can withdraw using the SWP (Systematic Withdrawal Plan) for the required amount at any time. Some debt schemes also offer the facility of ATM cards through which withdrawals can be done instantly.
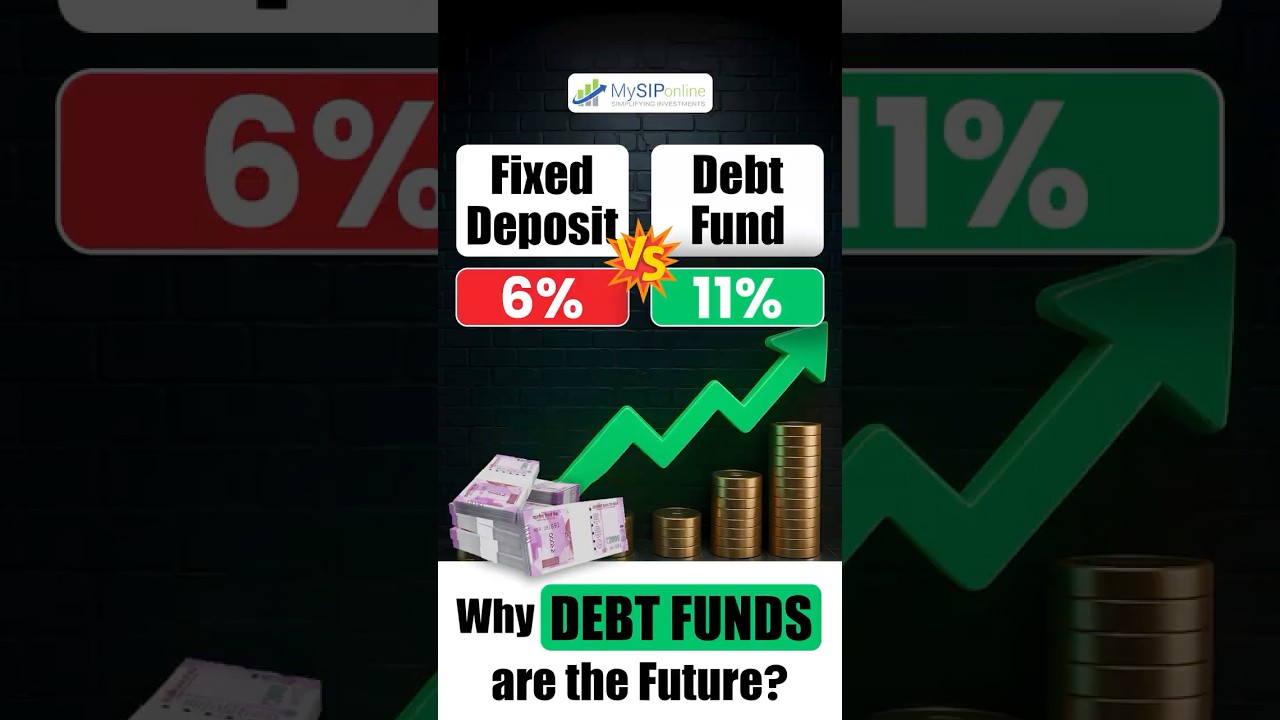
- Better Alternative to Bank Accounts: Debt mutual funds are a much better alternative to bank deposits and FDs or RDs. Keeping the cash in regular bank deposits provides 4% annual gains while the debt funds for short duration say liquid funds, offer 7-9% annual gains that are much higher. In FDs and RDs, redemption is not allowed at any time while the debt funds are open-ended.
Pro Tip: Calculate the withdrawal amount using the SWP Calculator with ease.
3 Best Debt Funds to Invest in 2026
Here are the 3 best-performing debt mutual funds to start your systematic investment plan with:
- ICICI Prudential Short Term Fund: After being launched on 1st October 2001, the ICICI Prudential Short Term Fund holds an AUM (Asset Under Management) at Rs.19.992 Crores. This fund falls under the short-duration funds category while giving an outstanding performance of delivering 7.84% CAGR since inception.
- Nippon India Nivesh Lakshya Fund: This fund belongs to long duration category under the fixed-income securities instruments. The Nippon India Nivesh Lakshya Fund was introduced on 5th July 2018 and since then it has delivered an impressive 8.88% CAGR while holding a robust AUM of Rs.9,111 Crores and can be a valuable addition to your portfolio in 2026.
- ICICI Prudential Gilt Fund: This fund started on 19th August 1999 and currently holds an AUM of Rs.6,771 Crores. This fund is best suited for you if you have zero tolerance for credit risk and it generates returns for you by investing a minimum of 80% of its investments in government securities. However, note that the interest rates are also quite high.
Who Should Invest in Debt Funds?
The following are some compelling reasons that make the debt mutual funds a good investment for 2026:
- Investors Seeking Regular Income: These funds are best suited if you have a low capacity for risk, for example, retirees who generally seek a steady income source with low risk.
- Conservative or First-Time Mutual Fund Investors: If you're new to investing or prefer low-risk options, short-duration funds or corporate bond funds can serve as a good alternative to bank fixed deposits, offering better returns and flexibility.
- Investors Wanting to Buy Equity in a Bearish Market: Aggressive equity investors can use debt funds with a Systematic Transfer Plan Calculator (STP) to move funds into equity during a market downturn, helping reduce average costs over time.
- Investors Looking to Park Short-Term Funds: If you have a short-term goal, you can consider liquid or ultra-short-duration funds, which offer better returns than bank deposits. These funds are also great for holding emergency funds while earning modest returns.
These debt funds have a versatile nature, a go-to alternative for conservative investors or anyone looking to complement their equity investments.
How to Invest in Debt Funds via MySIPonline?
Investing in debt funds through MySIPonline is simple and easy. Here’s how to get started:
- Open an Account: Create a free account on MySIPonline, fill out your profile and complete the KYC process.
- Set Up Auto-Debit: Register for automatic SIP deductions by setting up your debit mandate.
- Choose a Fund: Explore the best debt funds and pick the one that matches your investment goals.
- Make Your Purchase: Add your chosen fund to the cart, select the SIP date and complete the payment process.
- Monitor Your Investment: Track the performance and transaction details of your fund using the personalized dashboard.
Investing through SIP in debt mutual funds is a great way to build wealth over time with steady returns.
Other Categories of Mutual Funds
Frequently Asked Questions
Debt funds are a type of mutual funds that invest in bonds and government securities to provide stable income through interest and price appreciation.
Risks include interest rate risk (bond prices may fall when rates rise) and credit risk (default by issuers).
Debt Funds are ideal for conservative investors, those seeking regular income, or those prioritizing stability and capital preservation.
The types include liquid funds, short-term funds, corporate bond funds and gilt funds. Choose based on your investment time frame and risk tolerance.
Debt Funds offer low risk in comparison to equity funds but offer lower returns. They’re riskier than FDs due to market fluctuations but generally provide better returns.
Yes, debt funds allow you to withdraw your money by setting up a systematic withdrawal plan to automate monthly withdrawals.
Related Blogs & Videos
The related news, technologies, and resources from our team.
-1.webp)
-
544
-
7 Min. Read
.webp)
-
4032
-
9 Min. Read

-
2407
-
3 Min. Read

-
5152
-
10 Min. Read
 You can select three funds for compare.
You can select three funds for compare.